메모
전체 예제 코드를 다운로드 하려면 여기 를 클릭 하십시오.
Tripcolor 데모 #
구조화되지 않은 삼각형 그리드의 유사 색상 플롯.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.tri as tri
import numpy as np
삼각형을 지정하지 않고 삼각분할을 생성하면 점의 들로네 삼각분할이 됩니다.
# First create the x and y coordinates of the points.
n_angles = 36
n_radii = 8
min_radius = 0.25
radii = np.linspace(min_radius, 0.95, n_radii)
angles = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, n_angles, endpoint=False)
angles = np.repeat(angles[..., np.newaxis], n_radii, axis=1)
angles[:, 1::2] += np.pi / n_angles
x = (radii * np.cos(angles)).flatten()
y = (radii * np.sin(angles)).flatten()
z = (np.cos(radii) * np.cos(3 * angles)).flatten()
# Create the Triangulation; no triangles so Delaunay triangulation created.
triang = tri.Triangulation(x, y)
# Mask off unwanted triangles.
triang.set_mask(np.hypot(x[triang.triangles].mean(axis=1),
y[triang.triangles].mean(axis=1))
< min_radius)
삼색 플롯.
fig1, ax1 = plt.subplots()
ax1.set_aspect('equal')
tpc = ax1.tripcolor(triang, z, shading='flat')
fig1.colorbar(tpc)
ax1.set_title('tripcolor of Delaunay triangulation, flat shading')
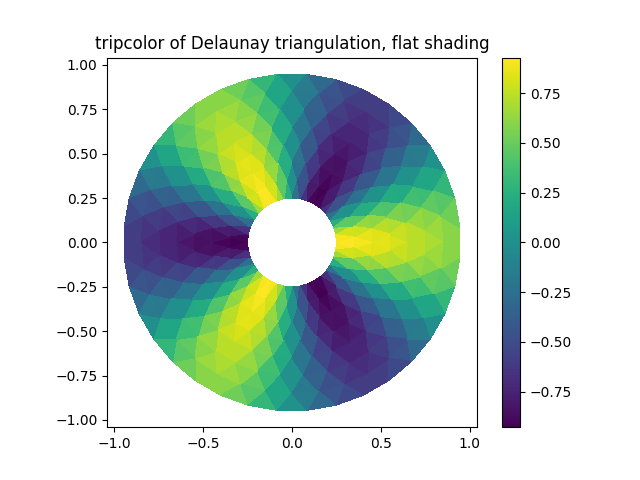
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'tripcolor of Delaunay triangulation, flat shading')
Gouraud 음영을 설명합니다.
fig2, ax2 = plt.subplots()
ax2.set_aspect('equal')
tpc = ax2.tripcolor(triang, z, shading='gouraud')
fig2.colorbar(tpc)
ax2.set_title('tripcolor of Delaunay triangulation, gouraud shading')
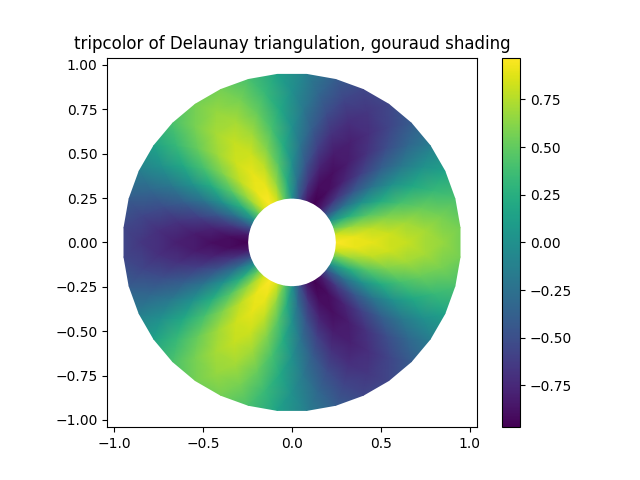
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'tripcolor of Delaunay triangulation, gouraud shading')
점의 Delaunay 삼각분할을 수행하는 대신 고유한 삼각분할을 지정할 수 있습니다. 여기서 각 삼각형은 시계 방향 또는 시계 반대 방향으로 정렬된 삼각형을 구성하는 세 점의 인덱스로 제공됩니다.
xy = np.asarray([
[-0.101, 0.872], [-0.080, 0.883], [-0.069, 0.888], [-0.054, 0.890],
[-0.045, 0.897], [-0.057, 0.895], [-0.073, 0.900], [-0.087, 0.898],
[-0.090, 0.904], [-0.069, 0.907], [-0.069, 0.921], [-0.080, 0.919],
[-0.073, 0.928], [-0.052, 0.930], [-0.048, 0.942], [-0.062, 0.949],
[-0.054, 0.958], [-0.069, 0.954], [-0.087, 0.952], [-0.087, 0.959],
[-0.080, 0.966], [-0.085, 0.973], [-0.087, 0.965], [-0.097, 0.965],
[-0.097, 0.975], [-0.092, 0.984], [-0.101, 0.980], [-0.108, 0.980],
[-0.104, 0.987], [-0.102, 0.993], [-0.115, 1.001], [-0.099, 0.996],
[-0.101, 1.007], [-0.090, 1.010], [-0.087, 1.021], [-0.069, 1.021],
[-0.052, 1.022], [-0.052, 1.017], [-0.069, 1.010], [-0.064, 1.005],
[-0.048, 1.005], [-0.031, 1.005], [-0.031, 0.996], [-0.040, 0.987],
[-0.045, 0.980], [-0.052, 0.975], [-0.040, 0.973], [-0.026, 0.968],
[-0.020, 0.954], [-0.006, 0.947], [ 0.003, 0.935], [ 0.006, 0.926],
[ 0.005, 0.921], [ 0.022, 0.923], [ 0.033, 0.912], [ 0.029, 0.905],
[ 0.017, 0.900], [ 0.012, 0.895], [ 0.027, 0.893], [ 0.019, 0.886],
[ 0.001, 0.883], [-0.012, 0.884], [-0.029, 0.883], [-0.038, 0.879],
[-0.057, 0.881], [-0.062, 0.876], [-0.078, 0.876], [-0.087, 0.872],
[-0.030, 0.907], [-0.007, 0.905], [-0.057, 0.916], [-0.025, 0.933],
[-0.077, 0.990], [-0.059, 0.993]])
x, y = np.rad2deg(xy).T
triangles = np.asarray([
[67, 66, 1], [65, 2, 66], [ 1, 66, 2], [64, 2, 65], [63, 3, 64],
[60, 59, 57], [ 2, 64, 3], [ 3, 63, 4], [ 0, 67, 1], [62, 4, 63],
[57, 59, 56], [59, 58, 56], [61, 60, 69], [57, 69, 60], [ 4, 62, 68],
[ 6, 5, 9], [61, 68, 62], [69, 68, 61], [ 9, 5, 70], [ 6, 8, 7],
[ 4, 70, 5], [ 8, 6, 9], [56, 69, 57], [69, 56, 52], [70, 10, 9],
[54, 53, 55], [56, 55, 53], [68, 70, 4], [52, 56, 53], [11, 10, 12],
[69, 71, 68], [68, 13, 70], [10, 70, 13], [51, 50, 52], [13, 68, 71],
[52, 71, 69], [12, 10, 13], [71, 52, 50], [71, 14, 13], [50, 49, 71],
[49, 48, 71], [14, 16, 15], [14, 71, 48], [17, 19, 18], [17, 20, 19],
[48, 16, 14], [48, 47, 16], [47, 46, 16], [16, 46, 45], [23, 22, 24],
[21, 24, 22], [17, 16, 45], [20, 17, 45], [21, 25, 24], [27, 26, 28],
[20, 72, 21], [25, 21, 72], [45, 72, 20], [25, 28, 26], [44, 73, 45],
[72, 45, 73], [28, 25, 29], [29, 25, 31], [43, 73, 44], [73, 43, 40],
[72, 73, 39], [72, 31, 25], [42, 40, 43], [31, 30, 29], [39, 73, 40],
[42, 41, 40], [72, 33, 31], [32, 31, 33], [39, 38, 72], [33, 72, 38],
[33, 38, 34], [37, 35, 38], [34, 38, 35], [35, 37, 36]])
xmid = x[triangles].mean(axis=1)
ymid = y[triangles].mean(axis=1)
x0 = -5
y0 = 52
zfaces = np.exp(-0.01 * ((xmid - x0) * (xmid - x0) +
(ymid - y0) * (ymid - y0)))
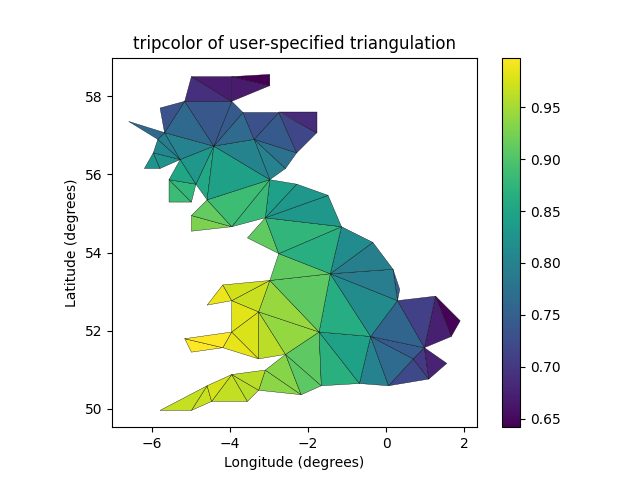
Triangulation 객체를 생성하는 대신 단순히 x, y 및 삼각형 배열을 tripcolor에 직접 전달할 수 있습니다. 중복된 계산을 저장하기 위해 동일한 삼각분할을 두 번 이상 사용해야 하는 경우 Triangulation 객체를 사용하는 것이 좋습니다. facecolors 키워드 인수 를 사용하여 점당 하나가 아닌 면당 하나의 색상 값을 지정할 수 있습니다.
fig3, ax3 = plt.subplots()
ax3.set_aspect('equal')
tpc = ax3.tripcolor(x, y, triangles, facecolors=zfaces, edgecolors='k')
fig3.colorbar(tpc)
ax3.set_title('tripcolor of user-specified triangulation')
ax3.set_xlabel('Longitude (degrees)')
ax3.set_ylabel('Latitude (degrees)')
plt.show()
참조
다음 함수, 메서드, 클래스 및 모듈의 사용이 이 예제에 표시됩니다.
스크립트의 총 실행 시간: ( 0분 1.930초)