메모
전체 예제 코드를 다운로드 하려면 여기 를 클릭 하십시오.
스택플롯 및 스트림 그래프 #
스택플롯 #
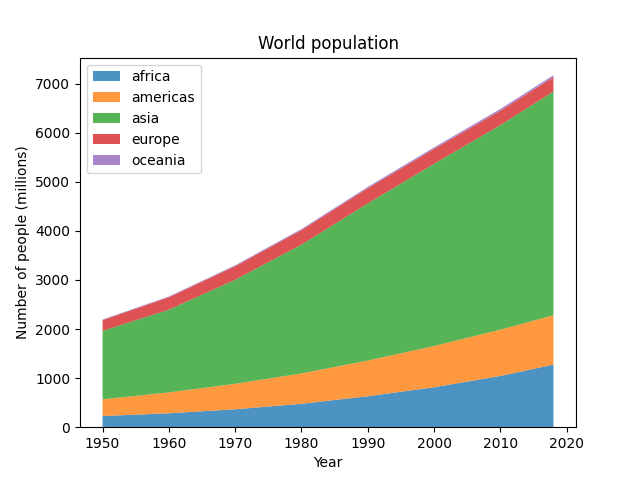
스택플롯은 수직으로 쌓인 영역으로 여러 데이터 세트를 그립니다. 이는 개별 데이터 값과 추가로 누적 값이 관심 있는 경우에 유용합니다.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# data from United Nations World Population Prospects (Revision 2019)
# https://population.un.org/wpp/, license: CC BY 3.0 IGO
year = [1950, 1960, 1970, 1980, 1990, 2000, 2010, 2018]
population_by_continent = {
'africa': [228, 284, 365, 477, 631, 814, 1044, 1275],
'americas': [340, 425, 519, 619, 727, 840, 943, 1006],
'asia': [1394, 1686, 2120, 2625, 3202, 3714, 4169, 4560],
'europe': [220, 253, 276, 295, 310, 303, 294, 293],
'oceania': [12, 15, 19, 22, 26, 31, 36, 39],
}
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.stackplot(year, population_by_continent.values(),
labels=population_by_continent.keys(), alpha=0.8)
ax.legend(loc='upper left')
ax.set_title('World population')
ax.set_xlabel('Year')
ax.set_ylabel('Number of people (millions)')
plt.show()
스트림 그래프 #
기준선 매개변수를 사용하면 기준선 이 0인 일반 누적 영역 플롯을 스트림 그래프로 전환할 수 있습니다.
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
def gaussian_mixture(x, n=5):
"""Return a random mixture of *n* Gaussians, evaluated at positions *x*."""
def add_random_gaussian(a):
amplitude = 1 / (.1 + np.random.random())
dx = x[-1] - x[0]
x0 = (2 * np.random.random() - .5) * dx
z = 10 / (.1 + np.random.random()) / dx
a += amplitude * np.exp(-(z * (x - x0))**2)
a = np.zeros_like(x)
for j in range(n):
add_random_gaussian(a)
return a
x = np.linspace(0, 100, 101)
ys = [gaussian_mixture(x) for _ in range(3)]
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.stackplot(x, ys, baseline='wiggle')
plt.show()