메모
전체 예제 코드를 다운로드 하려면 여기 를 클릭 하십시오.
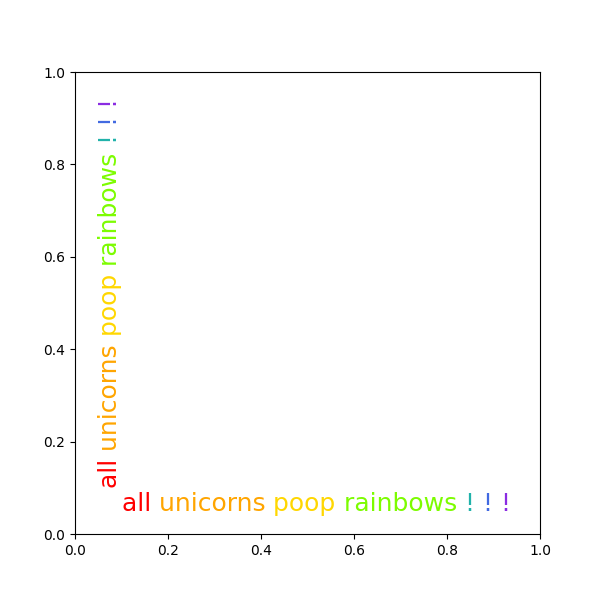
레인보우 텍스트 #
이 예는 여러 텍스트 객체를 함께 묶는 방법을 보여줍니다.
역사 #
2012년 2월 matplotlib-users 목록에서 Gökhan Sever는 다음과 같은 질문을 했습니다.
문자열의 색상을 부분적으로 지정하는 방법이 matplotlib에 있습니까?예시:plt.ylabel("오늘은 흐리다.")"오늘"을 빨간색으로, "is"를 녹색으로, "흐림"으로 표시하려면 어떻게 해야 합니까? 파란색으로?감사.
아래 솔루션은 Paul Ivanov의 원래 답변에서 수정되었습니다.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.transforms import Affine2D, offset_copy
def rainbow_text(x, y, strings, colors, orientation='horizontal',
ax=None, **kwargs):
"""
Take a list of *strings* and *colors* and place them next to each
other, with text strings[i] being shown in colors[i].
Parameters
----------
x, y : float
Text position in data coordinates.
strings : list of str
The strings to draw.
colors : list of color
The colors to use.
orientation : {'horizontal', 'vertical'}
ax : Axes, optional
The Axes to draw into. If None, the current axes will be used.
**kwargs
All other keyword arguments are passed to plt.text(), so you can
set the font size, family, etc.
"""
if ax is None:
ax = plt.gca()
t = ax.transData
fig = ax.figure
canvas = fig.canvas
assert orientation in ['horizontal', 'vertical']
if orientation == 'vertical':
kwargs.update(rotation=90, verticalalignment='bottom')
for s, c in zip(strings, colors):
text = ax.text(x, y, s + " ", color=c, transform=t, **kwargs)
# Need to draw to update the text position.
text.draw(canvas.get_renderer())
ex = text.get_window_extent()
# Convert window extent from pixels to inches
# to avoid issues displaying at different dpi
ex = fig.dpi_scale_trans.inverted().transform_bbox(ex)
if orientation == 'horizontal':
t = text.get_transform() + \
offset_copy(Affine2D(), fig=fig, x=ex.width, y=0)
else:
t = text.get_transform() + \
offset_copy(Affine2D(), fig=fig, x=0, y=ex.height)
words = "all unicorns poop rainbows ! ! !".split()
colors = ['red', 'orange', 'gold', 'lawngreen', 'lightseagreen', 'royalblue',
'blueviolet']
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
rainbow_text(0.1, 0.05, words, colors, size=18)
rainbow_text(0.05, 0.1, words, colors, orientation='vertical', size=18)
plt.show()