메모
전체 예제 코드를 다운로드 하려면 여기 를 클릭 하십시오.
pcolormesh #
axes.Axes.pcolormesh2D 이미지 스타일 플롯을 생성할 수 있습니다. 유사한 것보다 빠릅니다 pcolor.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import BoundaryNorm
from matplotlib.ticker import MaxNLocator
import numpy as np
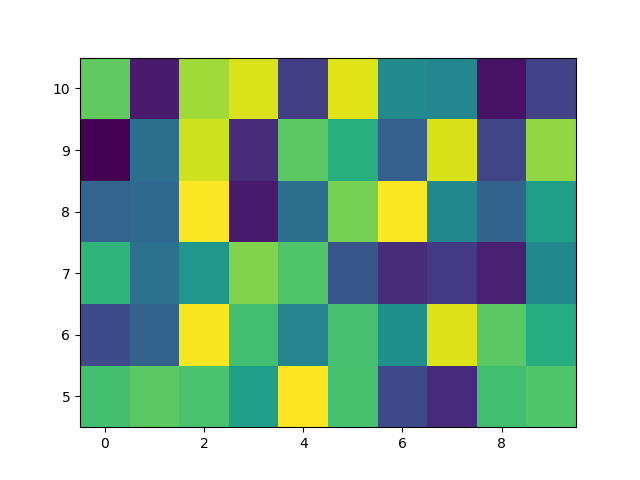
기본 pcolormesh #
우리는 일반적으로 사변형의 가장자리와 사변형의 값을 정의하여 pcolormesh를 지정합니다. 여기서 x 와 y 는 각각 해당 차원에서 Z보다 하나의 추가 요소를 가집니다.
np.random.seed(19680801)
Z = np.random.rand(6, 10)
x = np.arange(-0.5, 10, 1) # len = 11
y = np.arange(4.5, 11, 1) # len = 7
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.pcolormesh(x, y, Z)
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh object at 0x7f2d00aaeef0>
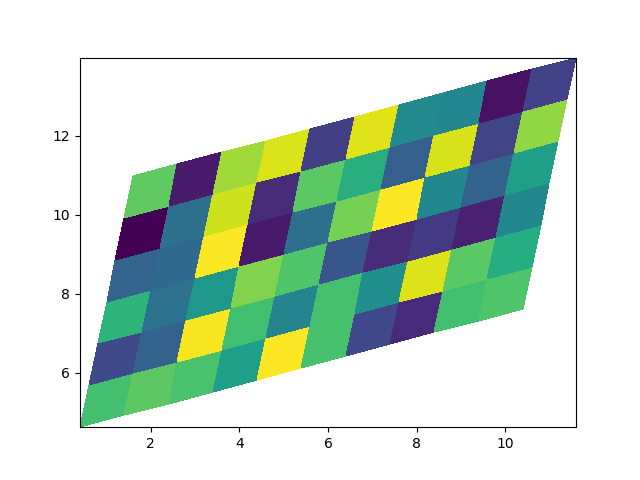
비직선 pcolormesh #
X 와 Y 에 대한 행렬을 지정할 수도 있고 비직선 사변형을 가질 수도 있습니다.
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh object at 0x7f2d00c610f0>
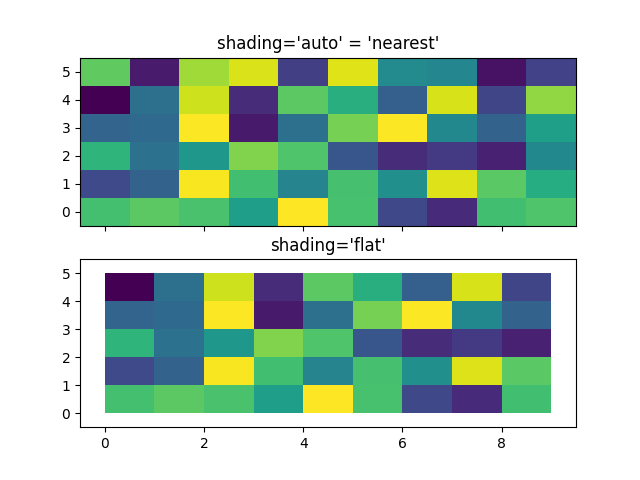
중심 좌표 #
종종 사용자는 Z 와 같은 크기의 X 와 Y 를 에 전달하려고 합니다
. 가 전달된 경우에도 허용됩니다 (기본값은 (기본값: )으로 설정됨). Pre Matplotlib 3.3에서는
Z 의 마지막 열과 행을 삭제합니다 . 이전 버전과의 호환성을 위해 여전히 허용되지만 DeprecationWarning이 발생합니다. 이것이 정말로 원하는 것이라면 Z의 마지막 행과 열을 수동으로 삭제하십시오.axes.Axes.pcolormeshshading='auto'rcParams["pcolor.shading"]'auto'shading='flat'
x = np.arange(10) # len = 10
y = np.arange(6) # len = 6
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=True, sharey=True)
axs[0].pcolormesh(X, Y, Z, vmin=np.min(Z), vmax=np.max(Z), shading='auto')
axs[0].set_title("shading='auto' = 'nearest'")
axs[1].pcolormesh(X, Y, Z[:-1, :-1], vmin=np.min(Z), vmax=np.max(Z),
shading='flat')
axs[1].set_title("shading='flat'")
Text(0.5, 1.0, "shading='flat'")
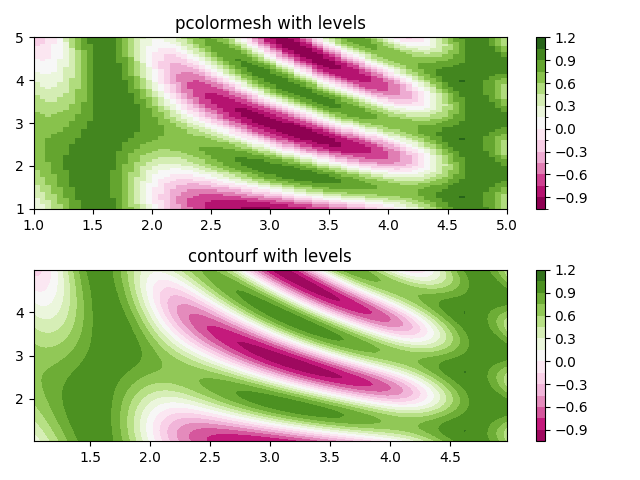
규범을 사용하여 레벨 만들기 #
Normalization 및 Colormap 인스턴스를 결합하여 에서 "레벨"을 그리는 axes.Axes.pcolor방법 과 contour/contourf에 대한 레벨 키워드 인수와 유사한 방식으로 플롯을 입력하는 axes.Axes.pcolormesh
방법 을 보여줍니다.axes.Axes.imshow
# make these smaller to increase the resolution
dx, dy = 0.05, 0.05
# generate 2 2d grids for the x & y bounds
y, x = np.mgrid[slice(1, 5 + dy, dy),
slice(1, 5 + dx, dx)]
z = np.sin(x)**10 + np.cos(10 + y*x) * np.cos(x)
# x and y are bounds, so z should be the value *inside* those bounds.
# Therefore, remove the last value from the z array.
z = z[:-1, :-1]
levels = MaxNLocator(nbins=15).tick_values(z.min(), z.max())
# pick the desired colormap, sensible levels, and define a normalization
# instance which takes data values and translates those into levels.
cmap = plt.colormaps['PiYG']
norm = BoundaryNorm(levels, ncolors=cmap.N, clip=True)
fig, (ax0, ax1) = plt.subplots(nrows=2)
im = ax0.pcolormesh(x, y, z, cmap=cmap, norm=norm)
fig.colorbar(im, ax=ax0)
ax0.set_title('pcolormesh with levels')
# contours are *point* based plots, so convert our bound into point
# centers
cf = ax1.contourf(x[:-1, :-1] + dx/2.,
y[:-1, :-1] + dy/2., z, levels=levels,
cmap=cmap)
fig.colorbar(cf, ax=ax1)
ax1.set_title('contourf with levels')
# adjust spacing between subplots so `ax1` title and `ax0` tick labels
# don't overlap
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
참조
다음 함수, 메서드, 클래스 및 모듈의 사용이 이 예제에 표시됩니다.
스크립트의 총 실행 시간: (0분 1.467초)